History
Our Vision
The History Department at Meadowhead aims to develop historians who are passionate about the past and equipped with skills for the future.
Our History Curriculum is designed to ensure that Meadowhead students:
- Are taught a coherent, balanced chronological narrative that gives them a knowledge and understanding of important periods and events in British and World History.
- Are taught a broad content that includes people of different genders, faiths and cultures in order to reflect the diversity of the school’s population and the diversity of wider British society.
- Are taught content that helps them to understand the modern world and current events and demonstrates how History is relevant to them today.
- Are taught engaging, challenging topics that they will enjoy studying.
- Develop and progress in their historical skills. Key concepts and skills required for GCSE will be integrated into lessons to aid their transition.
- Develop their writing skills and vocabulary.
- Have their needs met whatever their ability, background or educational needs so that it is accessible to all and inspirational for all.
“History is a light that illuminates the past, and a key that unlocks the door to the future.”
Runoko Rashidi
“We are not makers of history.
We are made by history.”Martin Luther King, Jr.
Key stage 3 (7-9)
Please click the hyperlinks to access the knowledge organisers
|
Year 7 |
Year 8 |
Year 9 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Term 1 |
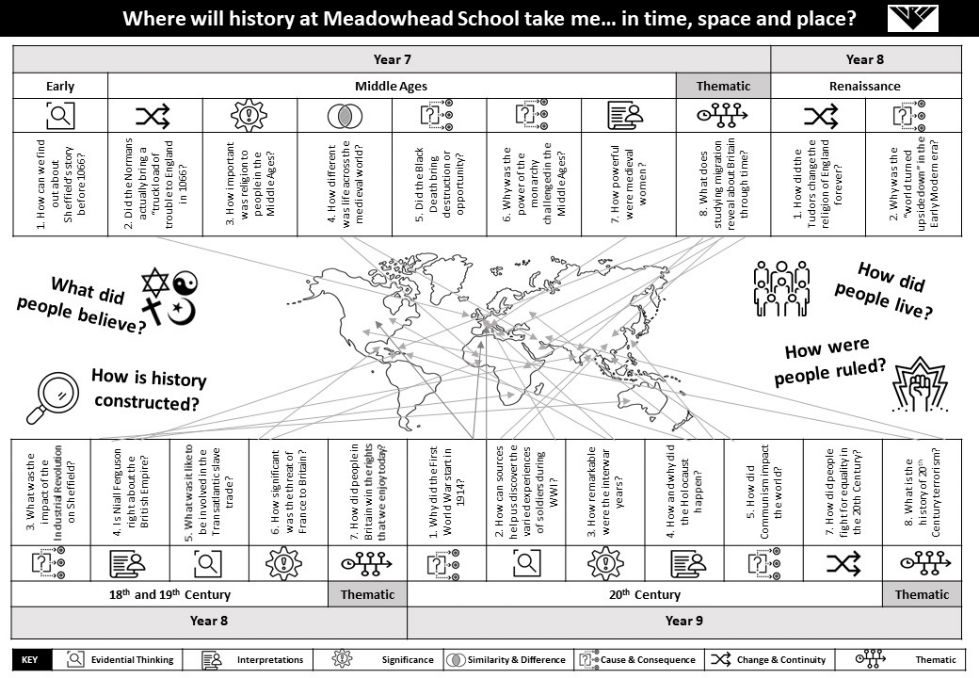
1. How can we find out about Sheffield’s story before 1066? (Evidential Thinking) 2. Did the Normans bring a “truckload of trouble” to England in 1066? (Change & Continuity) 3. How important was religion to people in the Middle Ages? (Historical Significance) |
1. How did the Tudors change the religion of England forever? (Change & Continuity) 2. Why did the way England was run change in the Early Modern Period? (Causation) |
1. Why did the First World War start in 1914? (Causation) 2. How can sources help us discover the varied experiences of soldiers during WWI? (Evidential Thinking) 3. How remarkable were the interwar years? (Significance) |
|
Assessment |
Enquiry Outcome Task for each enquiry Vocabulary and Knowledge Retrieval Tests for each enquiry |
Enquiry Outcome Task for each enquiry Vocabulary and Knowledge Retrieval Tests for each enquiry Assessment Week 1 – 20 Knowledge Retrieval Questions & Extended Answer |
Enquiry Outcome Task for each enquiry Vocabulary and Knowledge Retrieval Tests for each enquiry |
|
Term 2: |
4. How different was life across the medieval world? (Similarity & Difference) 5. Did the Black Death bring destruction or opportunity? (Consequence) 6. Why was the power of the monarchy challenged in the Middle Ages? (Causation) |
3. What was the impact of the Industrial Revolution on Sheffield? (Cause & Consequence) 4. Is Niall Ferguson right about the British Empire? (Interpretations) 5. What was it like to be involved in the slave trade? (Evidential Thinking)
|
4. How and why did the Holocaust happen? (Interpretations)
5. How did Communism impact the world? (Cause and Consequence) |
|
Assessment |
Enquiry Outcome Task for each enquiry Vocabulary and Knowledge Retrieval Tests for each enquiry Assessment Week 1 – 20 Knowledge Retrieval Questions & Extended Answer |
Enquiry Outcome Task for each enquiry Vocabulary and Knowledge Retrieval Tests for each enquiry Assessment Week 2 – 20 Knowledge Retrieval Questions & Extended Answer |
Enquiry Outcome Task for each enquiry Vocabulary and Knowledge Retrieval Tests for each enquiry Assessment Week 1 – 20 Knowledge Retrieval Questions & Extended Answer |
|
Term 3: |
7. How powerful were medieval women? (Interpretations) 8. What does studying Migration reveal about Britain through time? (Thematic)
|
6. How significant was the threat of France to Britain? (Significance) 7. How did British people win the rights that we enjoy today? (Thematic – Similarity & Difference) |
6. How did people fight for equality in the 20th Century? (Consequence) 7. What is the history of modern terrorism? (Thematic) |
| Assessment |
Enquiry Outcome Task for each enquiry Vocabulary and Knowledge Retrieval Tests for each enquiry
Assessment Week 2 – 20 Knowledge Retrieval Questions & Extended Answer |
Enquiry Outcome Task for each enquiry Vocabulary and Knowledge Retrieval Tests for each enquiry |
Enquiry Outcome Task for each enquiry Vocabulary and Knowledge Retrieval Tests for each enquiry Assessment Week 2 – 20 Knowledge Retrieval Questions & Extended Answer |
Key stage 4 (10-11)
|
Year 10 |
Year 11 |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Term 1 |
What was medicine like in the medieval period? How did medicine develop in the Renaissance? How did medicine develop in the 18th and 19th centuries? How did medicine develop in the 20th Century?
|
1. What were the origins of the Cold War? 2. What were the major crises in the Cold War? 3. How did Superpower relations change between 1945-91? |
|
Assessment |
20 knowledge questions + 20 mark question on Medieval and Renaissance medicine |
Mock Exams: Full Paper 1: Medicine Through Time & Historic Environment Full Paper 3: Weimar and Nazi Germany |
|
Term 2: |
Historic Environment: The British sector of the Western Front, 1914-18: injuries, treatments and the trenches. Was the Weimar Republic doomed to fail? |
1. How successfully did Elizabeth I rule England? KO: Queen, Government and Religion, 1558-69 2. What challenges did Elizabeth face at home and from abroad? KO: Challenges to Elizabeth at home and abroad, 1569-88 3. What was Elizabethan Society like in the Age of Exploration, 1558–88? |
|
Assessment |
20 knowledge questions + 20 mark question on Medicine in 18th, 19th and 20th Centuries |
Paper 2, Section A: Elizabethan England |
|
Term 3: |
Why did Hitler rise to power? How did Nazi control and the dictatorship develop? What was life like in Nazi Germany? |
Revision: Medicine through time Revision: Weimar and Nazi Germany |
|
Assessment |
Trial Exams: Full Paper 1: Thematic study and historic environment |
GCSE Examinations |
Key stage 5 (12-13)
|
Year 12 |
Year 13 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Term 1 |
1. The United States, 1917-33 2. The Roosevelt years, 1933-45 |
1. The response to apartheid, c1948-59 2. Radicalisation of resistance and the consolidation of National Party power, 1960-68 |
1. The British Navy and the French Wars 1793-1815 2. The British Army and French Wars 1793-1815 |
Coursework: : Reasons for the abolition of the slave trade |
|
Term 2: |
3. The affluent society, 1945-61 4. The changing political environment, 1961-9 |
3. Redefining resistance and challenges to National Party power, 1968-83 4. The end of apartheid and the creation of the ‘rainbow nation’, 1984-94 |
3. The Crimean War 1985-6 4. The Second Boer War 1899-1902 5. The First World War 1914-18 |
Coursework: Researching and writing coursework on the historiography around the abolition of the slave trade. |
|
Assessment |
Trials: Paper 1: Option 1F: In search of the American Dream: the USA, c1917–96 |
Trials: Paper 2: Option 2F.2: South Africa, 1948–94: from apartheid state to ‘rainbow nation’ |
Trials: Paper 3: Option 35.2: The British experience of warfare, c1790–1918 |
Coursework submitted: 3000-4000 word essay on What were the justifications for Britain’s involvement in the Slave Trade and how did it work? |
|
Term 3: |
5. A decline in confidence, 1968-80 Background to coursework: What were the justifications for Britain’s involvement in the Slave Trade and how did it work? |
6. Historical interpretations: What impact did the Reagan presidency have on the USA, 1981-96? |
Revision |
Revision |
|
Assessment |
Assessment week / resit trials: Paper 1 |
Paper 2: |
Resit trials | N/A |
Useful websites
https://qualifications.pearson.com/en/qualifications/edexcel-gcses/history-2016.html
https://qualifications.pearson.com/en/qualifications/edexcel-a-levels/history-2015.html
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/subjects/zj26n39
https://www.senecalearning.com/
Extra-curricular / enrichment
- A range of Historic environment visits will be offered to narrow the ‘cultural gap’ and enhance cultural capital:
- Peveril Castle
- Battlefields in France and Belgium
- Royal Armouries in Leeds
- Washington DC
- Weekly History Film Club for KS3 to further engage students in the subject.
- Cross-age mentoring for GCSE students to help them with revision, examinations and responsibility.
- One off events and visiting speakers for key commemorations/themes.

Battlefields trip